User-centered design (UCD) prioritizes real users’ needs throughout the project design and development. It begins with examining the needs and preferences of specific users to design products that lead to exceptional performance, better experiences, stronger brand loyalty, and measurable business growth. This blog drives you through a comprehensive exploration of user-centered design, its principles, benefits, process of implementation, challenges and solutions, real-life examples, and the future.
88% of users are less likely to return after a bad user experience. Yes, and that’s where user-centered design comes into play. It is a strategy that prioritizes users’ needs and preferences throughout the design process to develop a product that aligns with the users’ expectations.
In today’s digital-first world of fierce competition, creating products tailored to users’ needs is no longer optional but essential. Popular products like Slack, Trello, Mailchimp, and many more adopt a user-centered design to bring their services in alignment with their users’ needs, thereby unleashing opportunities to grow.


From intuitive interfaces to seamless user flows and exceptional experiences, UCD ensures that every design decision is rooted in empathy and usability, making the product relatable to users’ needs. Through this blog, you’ll learn everything about user-centered design to be ready to implement it into your project and get the most out of your product development.
What is User-Centered Design (UCD)?
Unlike human-centered design, user-centered design (UCD) is a design philosophy of understanding the needs and preferences of a specific set of users to meet them appropriately. UCD follows an iterative process that involves analyzing users’ needs and behaviors and incorporating that feedback throughout the product design to improve the product continually. User-centered design aims to make products, services, and processes accessible, usable, and satisfactory enough for target users.
Significant Aspects of UCD:
- User Research: User-centric design involves collecting information relating to users’ needs, behaviors, and context of the user through interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
- User Focus: UCD makes sure that the product or service is designed keeping users’ needs in mind.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Designers make decisions based on data and insights collected from user research, ensuring the products remain aligned with the user’s requirements.
- Iterative Approach: UCD isn’t a one-time process but a cycle of product design, testing, and refinement according to the user’s feedback.
What are the Core Principles of User-Centered Design?
Key principles of user-centered design include empathy, user involvement, an iterative approach, and understanding the context of use. UCD aims to create products and experiences that are user-friendly, intuitive, and meet users’ specific requirements.
- Empathy: Understanding the user’s perspective, such as their needs, emotions, and motivations, by putting yourself in the audience’s shoes to create relatable and satisfying experiences.
- Research: Conducting thorough research to know the pain points of users and provide a satisfactory solution to meet their needs.
- User Personas: Creating user personas that let designers understand user needs, goals, and motivations, which in turn guide design decisions throughout the product design process.
- Early and Frequent User Involvement: Involving users early and keeping them throughout the design process. It starts from the early stages to testing and iteration.
- Prototyping: Creating interactive wireframes or mockups to simulate the flow and functionality of a product.
- Iteration Based on Feedback: Accumulating and incorporating user feedback in the design process to refine the design and align it with the user’s goal and expectations.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Making decisions based on data gathered from user research and testing.
- Usability Testing: Conducting thorough testing and making sure the design is capable of meeting the user’s requirements.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensuring that user needs and business goals are well aligned. This involves striking a balance between user satisfaction and business objectives.
Steps to the User-Centered Design Process
User-centered design (UCD) involves understanding users’ needs, defining their requirements, creating design solutions, and measuring their effectiveness, all while keeping the user at the center of the design process. Here are the steps for user-centered design you should know before getting started:
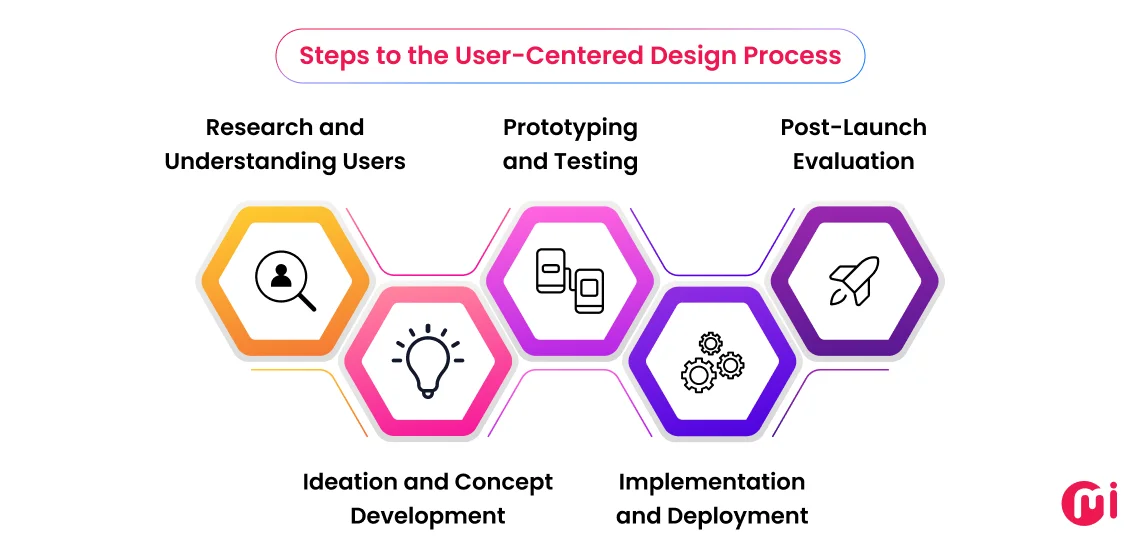

1. Research and Understanding Users
- Empathizing: It’s an act of going beyond data and truly understanding and sharing users’ needs, feelings, and perspectives to create a product or service that resonates with their needs. It lets designers create solutions that are intuitive, effective, and satisfying for the end-user.
- User Research: This phase involves gathering information relating to the target users, their challenges, behaviors, and motivations. User research includes interviews, surveys, user testing, and ethnographic studies.
- Defining User Personas: It includes identifying patterns and segmenting users based on the insights from user research, creating distinct groups to represent key user types. Eventually, designers flesh out each persona with detailed profiles, which involve motivations, demographics, and typical scenarios, making them actionable and relatable.
- Requirement Specifications: This phase deals with translating research insights into concrete project requirements. Requirement specifications involve defining what the product must do, aligning business goals and user needs, and outlining technical limitations.
2. Ideation and Concept Development
- Generating Ideas: It involves promoting open-ended thinking to create innovative design solutions. Conducting workshops with stakeholders and designers assists in refining ideas that align with the project’s goals as well as user expectations.
- Creating Wireframes and Mockups: In this stage of the user-centered design, the team brainstorms and creates potential solutions to the defined problem. It includes creating wireframes and mockups.
3. Prototyping and Testing
- Creating Prototype: In this step, designers create tangible prototypes to test their ideas and user interactions early on in the design process. Through prototyping, they get a quick identification of potential usability issues, limiting the risk of expensive redesign and development errors down the line.
- Conducting Usability Testing: It includes testing how real users interact with your prototype, gaining feedback, and iterating on the design to fix issues and enhance usability.
- Iterating on Design: This phase includes iterating on designs based on users’ feedback for continuous improvement and refinement. The process is a cycle of collecting feedback, analyzing it, making changes, and testing those changes again and again for optimal performance.
4. Implementation and Deployment
- Final Product Development: In this phase, designers work on implementing the method and developing the final product. In this very phase, they ensure the design vision is brought to life in the final product with optimal accuracy.
- Product Deployment: Once the design is created appropriately, the experts work on the deployment of the product.
5. Post-Launch Evaluation
- Feedback Gathering: It includes collecting user feedback through analytics, surveys, reviews, and interviews to gain an understanding of user experience and identify areas in need of enhancement.
- Performance Analysis: This phase involves measuring user engagement, retention, task completion rates, and additional KPIs, aiming to evaluate usability and success.
- Iteration and Refinement: In this phase, experts make use of insights from the evaluation to make necessary updates, fix usability issues, and boost the product in future releases.
What are the Benefits of User-Centered Design?
User-centered design (UCD) provides numerous benefits, focusing on improved product accessibility, usability, and enhancing user experience and satisfaction. It leads to building products that are easy to use, more intuitive, and meet users’ specific needs. A user-centered design approach also boosts user engagement and retention and fosters a competitive edge by creating a superior user experience. Here’s a detailed look at the benefits of UCD design:
Enhanced Accessibility
User-centered design significantly enhances accessibility by focusing on user needs and using their feedback throughout the design process. By prioritizing accessibility requirements from the outset, UCD ascertains that the product is usable by all the targeted users in diverse situations. It results in better engagement and user retention, fostering enhanced revenue and growth.
- Understanding users’ needs
- Involving users
- Addressing accessibility standards
- Designing for diverse abilities
Increased Usability
A user-centered design approach enhances product usability by focusing on the needs, preferences, and behaviors of the end-users throughout the design process, ultimately leading to more intuitive, efficient, and satisfying experiences. This approach ensures that products are easier to learn, use, and navigate, reducing frustration and increasing user satisfaction.
- User involvement and feedback
- Understanding users’ expectations
- Creating intuitive interfaces
- Enhanced product usability
Improved User Satisfaction
A user-centered design method significantly improves user satisfaction, as it prioritizes user needs and preferences and involves them throughout the design process. The very approach to product design leads to high-end products and interfaces that are more accessible, intuitive, and enjoyable to use. This way, UCD results in improved user satisfaction, positive brand perception, and a significant boost in loyalty.
- Focus on user needs
- Focus on usability
- Interactive development
- Seamless user experience
Higher Engagement and Retention
User-centered design (UCD) boosts higher engagement and retention by prioritizing what users actually require. The UI/UX engineers involve users in the design process to be aware of what users expect to create products that are easy to use and intuitive, leading to improved user satisfaction. This way, users are propelled to use a product more and more, fostering skyrocketed engagement and retention.
- Increased accessibility
- Improved usability
- Excellent user satisfaction
- Higher engagement and retention
Excellent User Advocacy
User advocacy promotes sales with the competencies of word-of-mouth marketing, providing authentic content, and referrals. By satisfying customers who willingly promote a brand, organizations can build trust and boost brand awareness, thereby leading to skyrocketing sales and revenue.
- Authentic word-of-mouth content
- Lead generation and conversion
- User-generated content (UGC)
- Increased sales and revenue
Reduced Development Costs
A user-centered design approach reduces development costs by incorporating user feedback throughout the design process. It proactively addresses usability issues and aligns user needs with the design process, hence minimizing the need for expensive redesigns or rework later. This proactive approach to product design leads to reduced chances of changes down the line, which could otherwise be more time-consuming and expensive.
- Early issue identification
- Prioritizing features
- Limiting redesign needs
- Reduced development cost
Competitive Advantage
User-centered design provides businesses with a competitive advantage by focusing on and meeting user needs in product design. It leads to products and services that are well-functional, easy to use, and intuitive, ultimately creating a positive user experience and boosting brand loyalty. Here is how it works:
- Differentiation in the market
- Exceptional user experience
- Better control over the user base
Real-Life Examples of User-Centered Design
Some of the real-life user-centered design (UCD) examples involve the intuitive interface of Slack and the excellent usability of Mailchimp’s email marketing platform. The extraordinary visual organization of Trello’s project management tool and Fitbit’s wearable fitness technology can also be considered good examples of UCD. The following examples demonstrate the way prioritizing user needs leads to excellent projects and high-end success.
1. Slack: Collaboration Made Effortless
Slack is an excellent example of user-centered design. It prioritizes understanding user needs, gathering feedback, and implementing them to ensure that the solution is highly usable, interactive, and intuitive. UCD makes Slack easy to use, fostering its success in the marketplace.
Slack’s user-centered design highlights:
- User Feedback Loops: Consistent updates based on user behavior and requests.
- Intuitive Interface: Channels, threads, and search are streamlined to reduce clutter.
- Customization: Users can tailor notifications, themes, and integrations based on their preferences.
- Accessibility: Keyboard shortcuts, screen reader support, and status customization improve usability for all users.
2. Mailchimp: Empowering Non-Designers
Mailchimp is an excellent example of user-centered design. Its drag-and-drop interface and robust automation tools are excellently designed to be user-friendly, even for those with limited technical knowledge. Mailchimp iterates designs based on user feedback and involves users throughout the design process, aiming to yield user-friendly solutions.
Mailchimp’s user-centered design highlights:
- Feedback-Informed Features: Iterations according to the continuous user testing and data.
- Simplified Workflow: Step-by-step guidance to create email campaigns.
- Clear Language: Friendly and non-technical microcopy fosters user confidence.
- Onboarding Support: Demos, tooltips, and templates limit the learning curves.
3. Trello: Visual Task Management
One of the excellent examples of user-centered design is Trello, which simplifies task management through its visual, card-based interface for users. This makes it easy for teams to collaborate and keep track of progress. Trello focuses on ease of use and intuitive workflows, which is evident in its simple structure, flexible board customization, and exceptional visual aesthetic, making it an exceptional choice for teams of different types.
Trello’s user-centered design highlights:
- Visual Clarity: Drag-and-drop interface that matches natural workflows.
- Flexible Use Cases: Better for individuals, teams, or cross-functional projects.
- User Empowerment: Power-ups and integrations adapt Trello to cater to user-specific needs.
- Feedback-Driven Updates: Features evolve as per the community input and beta testing.
4. Fitbit: Health Tracking with Empathy
Fitbit’s wearable fitness technology is designed for a wider range of fitness goals and lifestyles, making it the right choice for health-conscious individuals. It prioritizes user experience, incorporates feedback, and creates customized features to appeal to a wider range of fitness goals and lifestyles. Fitbit focuses on simplicity, utility, and continuous improvement according to the user’s data and makes fitness tracking accessible for diverse populations.
Fitbit’s user-centered design highlights:
- Data Visualization: Simple, visual dashboards to keep track of steps, sleep, and heart rate.
- Personal Goals: Allows customizing fitness goals for different user lifestyles.
- Daily Engagement: Encouraging nudges and reminders aligned with behavior patterns.
- Inclusive Design: Devices and apps are usable for a wider demographic, including older adults.
Challenges in UCD and How to Overcome Them
There are numerous benefits of implementing user-centered design; however, there are also some challenges associated with it that you may encounter. The following are a few of the challenges and their solutions for UCD implementation:
1. Balancing User Needs and Business Goals
Aligning users’ requirements with business goals can be complex, requiring trade-offs.
Solution: Organizations should communicate the business value of UCD, include stakeholders early in the process, and focus on solutions that align with both business objectives and users’ needs.
Example: Businesses could demonstrate how user-centered design can lead to improved product and service quality, increased user satisfaction, and reduced costs.
2. Managing User Feedback and Research
It can be challenging to encourage active user participation because of time constraints, disinterest, or a lack of expertise.
Solution: Organizations should use diverse feedback methods like interviews, surveys, and observations, and make it easy for users to participate in online surveys and in-person sessions, and offer incentives for involvement.
Example: Businesses can provide gift cards or other incentives for participating in user research.
3. Time and Budget Constraints
Conducting intensive user research, designing prototypes, and collecting feedback are more likely to be time-consuming and expensive.
Solution: Businesses should consider prioritizing essential UCD activities, using agile methodology and lean methods, and focusing on providing incremental and iterative solutions.
Example: Irrespective of conducting extensive user research upfront, businesses can prioritize obtaining key insights and gathering feedback throughout the design process.
4. Finding the Right Partner
Finding and collaborating with the inappropriate design or development partner might misalign your user-centric design goals. It could lead to wasted resources, poor user experiences, and missed business objectives.
Solution: Businesses should look for partners with proven expertise in user-centered design, a robust and reliable portfolio of user-focused solutions, and a collaborative mindset. They should intensively evaluate the approach of a service provider towards empathy, research, testing, and iteration to make sure they align with users’ values and business goals.
Example: Instead of choosing a design company based solely on cost or speed, businesses should hire UI/UX designers who can demonstrate successful case studies in UCD, showcase transparency in their process, and involve users and stakeholders in the design cycle for an exceptional outcome.
The Future of User-Centered Design
The future of user-centered design includes making use of emerging technologies, such as AI, to create personalized, predictive, and inclusive user experiences; AI VR for immersive environments; and many more. It also focuses more on ethical considerations and adaptability to constantly evolving user behaviors and preferences. See the pointers below to see the prospective future of user-centric design:
- AI and ML integration: AI and ML will play a crucial role in elevating the user-centered design process, promoting predictive user experiences and personalized recommendations.
- Augmented and virtual reality: Integrating augmented and virtual reality will introduce additional challenges and opportunities for UCD in immersive environments.
- Beyond screens and workflows: UX designers will be evolving into strategic leaders, guiding AI-enabled designs and translating intense user insights into meaningful experiences.
- AI-enabled personalization: AI will be used to analyze a wide range of user data to create highly tailored experiences, customizing content, features, and the user interface to individual preferences.


Choose us to Transform Your Project with User-Centered Design
User-centered design brings numerous benefits; however, it becomes icing on the cake when you’ve the right UI/UX design company working on your project. And that’s where MindInventory comes into the picture.
We’re a team of vetted UI/UX designers, having provided 450+ design projects across 90+ countries. We help businesses create user-centered design solutions that best fit their users’ needs.
Be it web design, mobile app design, SaaS product design, digital product redesign, or just UI/UX design consulting, we provide all you may need to bring your ideas to life.
So, if you have a project and you need user-centered design, feel free to contact us and choose us as your product design partner to ensure you build a product for visible growth and ROI.
FAQs on User-Centered Design
The 4 primary design elements are empathy, data-driven decision-making, early and continuous testing, and iteration according to user feedback.
User-centric design is an approach that focuses on user needs and involvement in the design and development process to ensure products are usable and meet user goals. On the other hand, UX is the broader concept about how a user interacts with and experiences a product or service. It might involve their perception of utility, efficiency, and ease of use. In conclusion, UCD is a methodology, while UX is the result of employing that methodology.
No, user-centric design isn’t exclusive to large companies. It’s an invaluable approach for different organizations, irrespective of their size, including small businesses and startups.